Getting started with CityJSON
Table of contents
- Download a simple file with 2 buildings
- Visualise it
- Manipulate and edit it with cjio
- What else?
- Questions and need help?
Download a simple file with 2 buildings
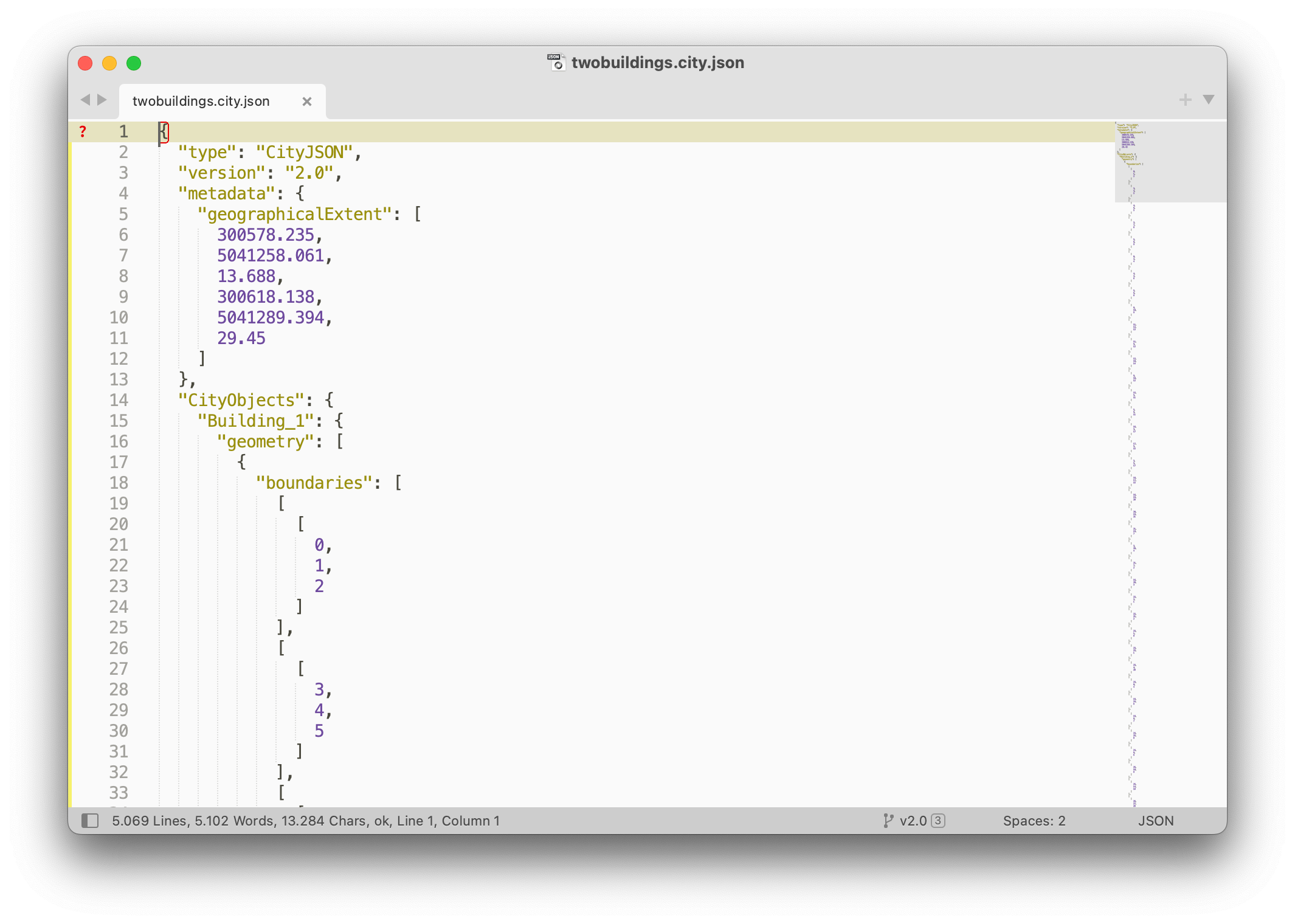
Download twobuildings.city.json, a simple file with 2 buildings.
You can open that file in any text editor to see its structure, and notice that you can manually edit it to change values and/or add new buildings, new metadata, or delete some attributes.
Visualise it
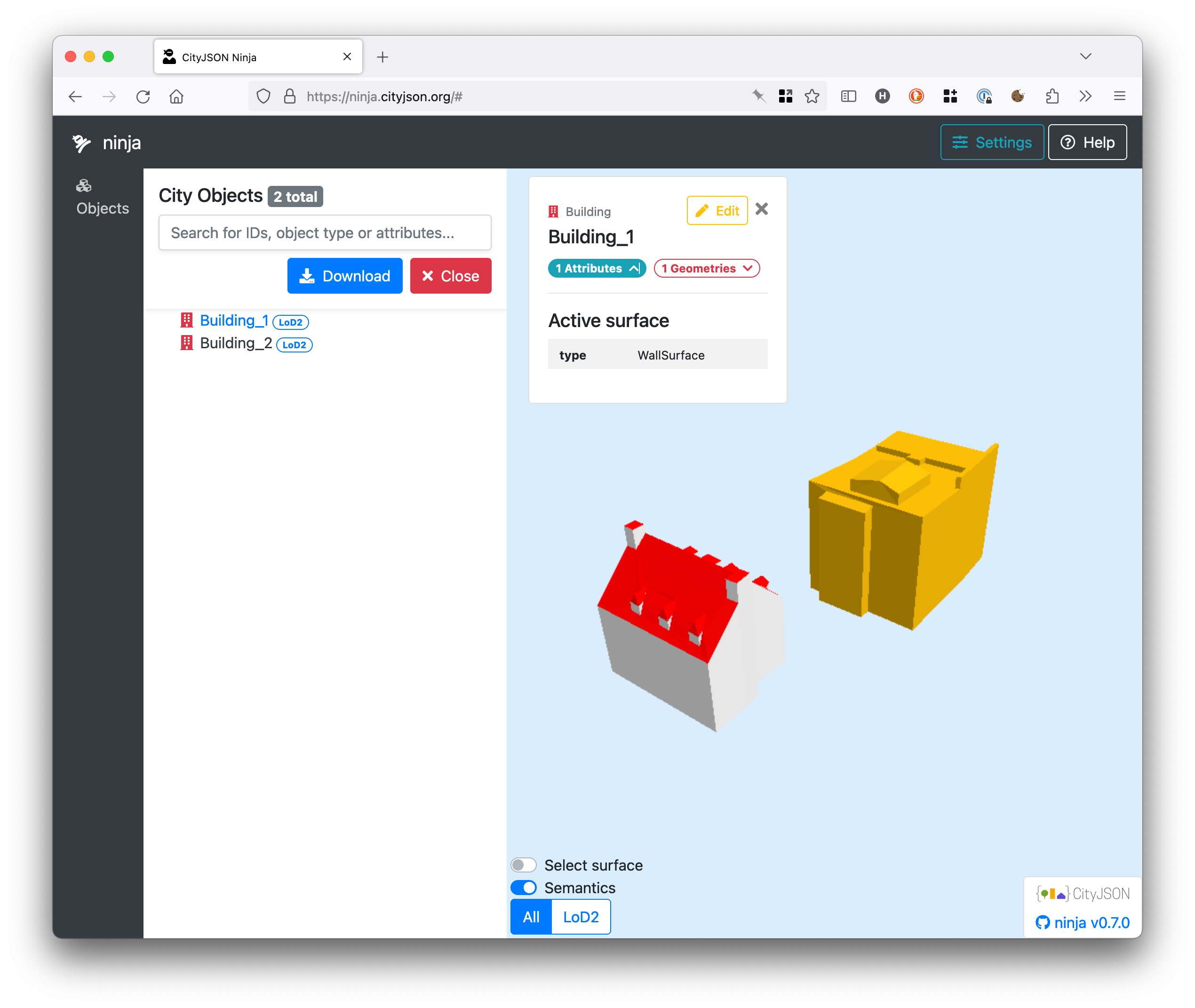
Go to the CityJSON official online viewer (called ‘ninja’) and drop the file, and voilà:
Manipulate and edit it with cjio
Manually editing a file is error-prone, so instead you can use cjio. It can be used to manipulate, edit, and validate CityJSON files.
You must have Python (version >3.7) installed, and pip.
cjio is a command-line interface program, which means that there is no graphical user interface and that you need to use the console (also called the “Command Prompt”, or the terminal).
To install the latest release:
pip install cjio
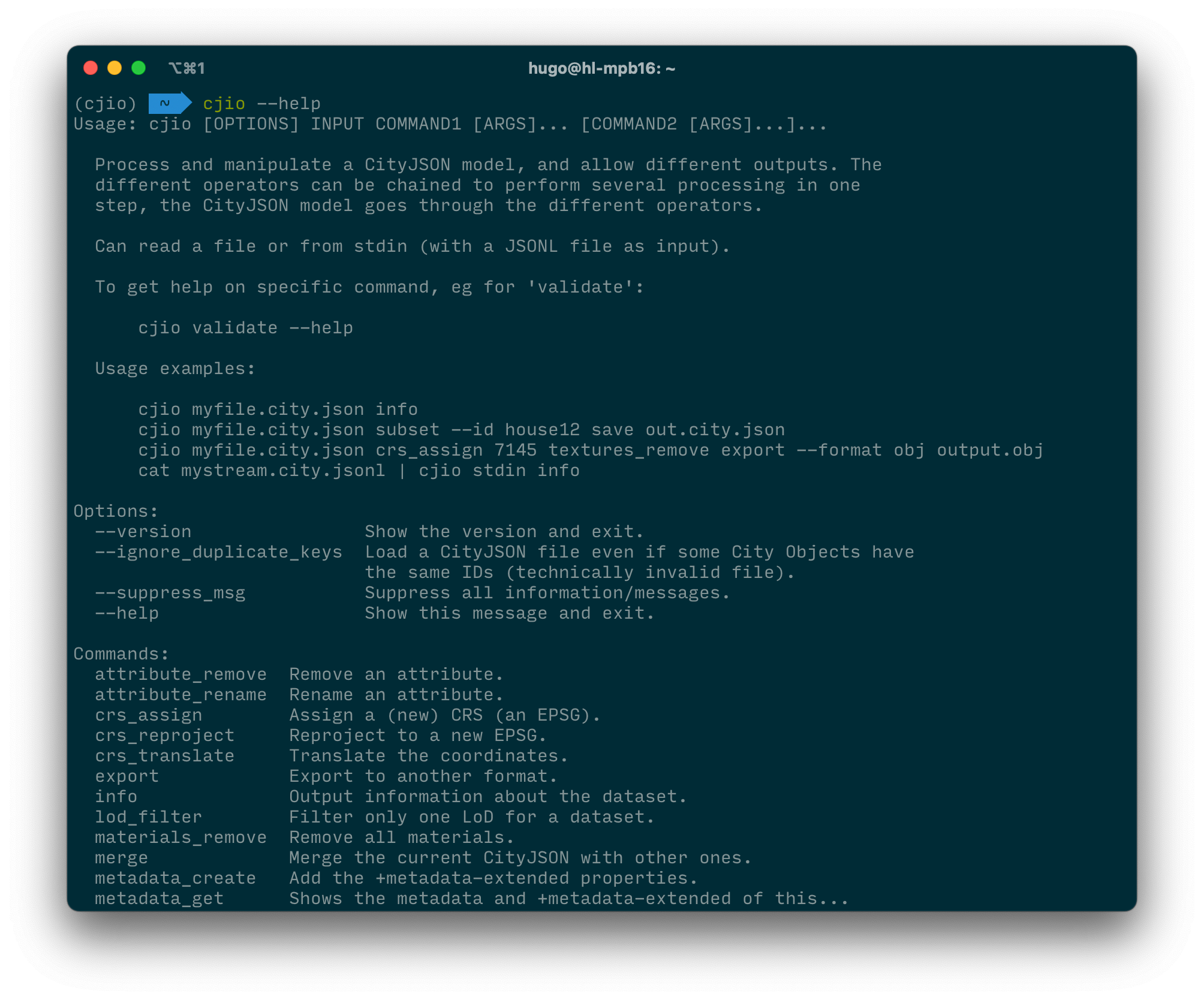
After the installation, you have a small program called cjio, to see its possibilities type cjio --help and it should print all the options, as shown here:
To get some general information about the file you downloaded, navigate to the folder where it is located, and type:
cjio twobuildings.city.json info
and you should get this output:
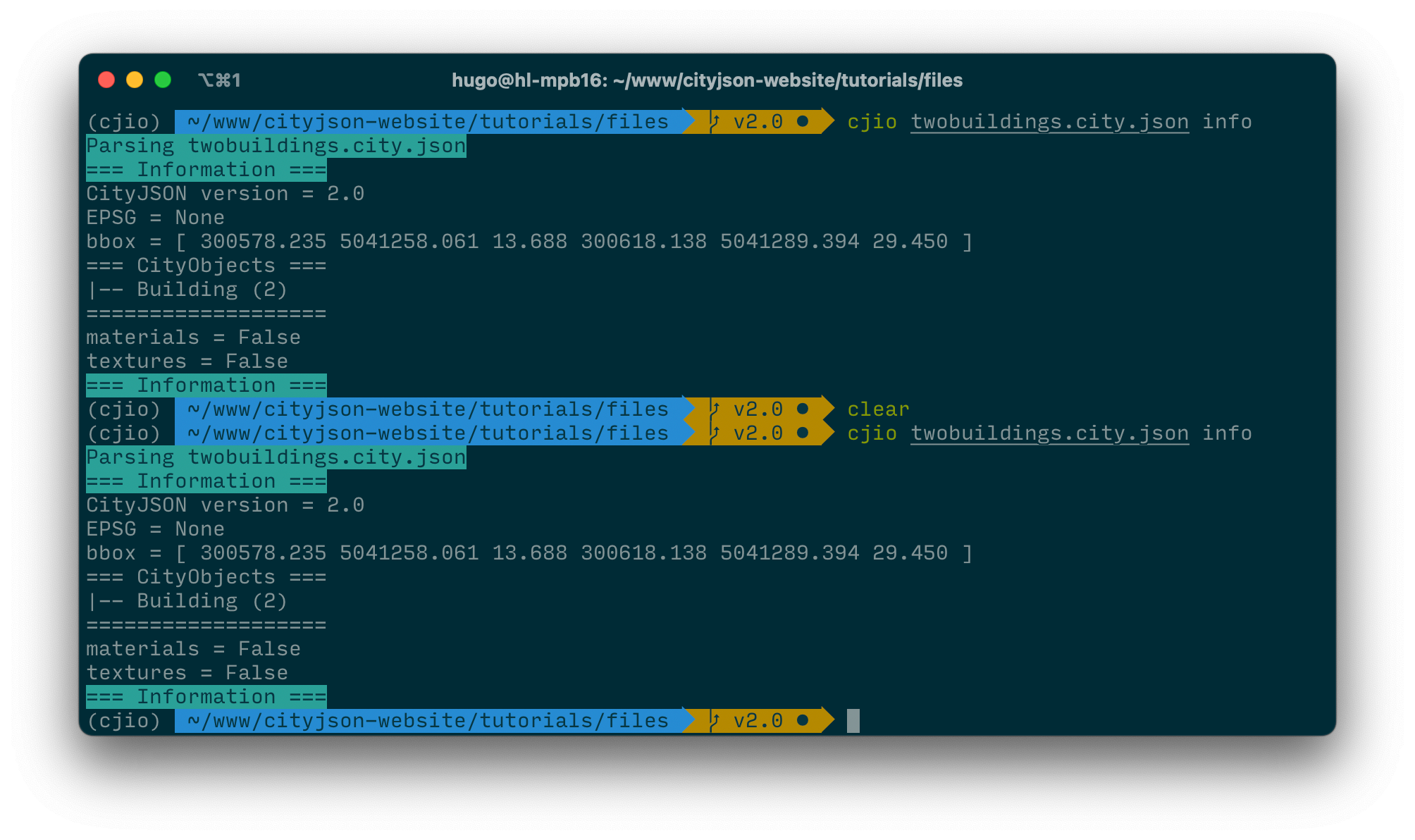
Observe that the EPSG is None. To assign an EPSG to the file (26918 is the value, that dataset is part of the Montréal open 3D dataset), you can type:
cjio twobuildings.city.json crs_assign 26918 save twobuildings_reprojected.city.json
Notice that 2 cjio operators are used in one command: crs_assign and save. The first one assigns the CRS to the file, and the second allows us to save the file on disk (in the current folder).
If you then type cjio twobuildings_reprojected.city.json info you should see that now an EPSG is assigned to 3D city model.
The cjio operators can be linked in a pipeline, and the 3D city model opened is passed through all the operators, and it gets modified by some operators. Operators like info and validate output information in the console and just pass the 3D city model to the next operator.
Some examples:
$ cjio example.city.json subset --id house12 info materials_remove info save out.city.json
$ cjio example.city.json attribute_remove roofType save new.city.json
$ cjio myfile.city.json merge '/home/elvis/temp/*.json' save all_merged.city.json
What else?
One important point is ensuring that the files you produce and manipulate are valid, see our validation tutorial to learn how to do this (for the schema and the geometric primitives).
Several datasets can be downloaded from the datasets page, but more importantly, it is possible to convert any CityGML file, see our tutorial.
Questions and need help?
CityJSON has its own forum, don’t hesitate to ask if you’re struggling with reading/manipulating/creating CityJSON datasets.